Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
Professor Merserkinger - father of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery with Dr Stanley in Graz, Austria 1991.
Hands-on Laboratory Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Course, Graz, Austria
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery – a form of minimally invasive transnasal surgery to drain and re-inventilate the paranasal sinuses.
Dr Stanley underwent an intensive hands-on instructional course / Laboratory Training by founders of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery, Prof. Merserklinger and Prof. Heinz Stamberger at Graz Austria in 1991.
Dr Stanley developed a keen interest in Endoscopic Sinus Surgery including the treatment of skull lesions as in advanced endoscopic sinus surgery.
Several thousands of Endoscopic Sinus procedures have been performed to date and has been extended for anterior and central skull base lesions.
Outpatient Endoscopy - Flexible
Diagnostic Rigid Nasoendoscopy
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery is only offered after failure of maximal medical therapy for chronic sinusitis.
A conservative approach is done on children in addition to an adenoidectomy when indicated.
Paediatric Endoscopic Sinus Surgery is a last resort for children suffering from Sinusitis after failure of medical therapy.
If performed, a mini-FESS (Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery) technique is performed to promote ventilation and drainage of the osteo-meteal complex.
Thorough evaluation of CT Scans are essentials
Final evaluation after failure of maximal medicinal treatment with CT Scans of the sinuses being examined. The extent of surgery and inherent variations of anatomy are assessed pre-operatively. Risks are minimised by proper evaluation of the CT Scans pre-operatively to identify danger areas in the patients anatomy.
Blocked Osteo-Meatal Complex Before Surgical Treatment of Chronic Sinusitis
A mini FESS procedure with middle meatal antrostomies to drain and ventilate the maxillary sinuses is the minimum procedure required. This is usually performed in children and occasionally in adults.
Surgical Created Antrostomics After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (Mini FESS)
Endoscopic Drainage of Ethmoidal Mucocele
Before operation
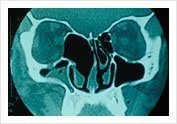
Scan before operation Mucocele in Ethmoid
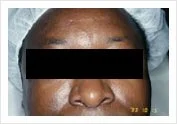
An ethmoidal mucocele (collection of thick fluid in a sinus cavity) causing exophthalmos (bulging of the eyeball).
Endoscophic Drainage of Ethmoidal Mucocele during and end of operation
Endoscophic Drainage of Ethmoidal Mucocele during and end of operation
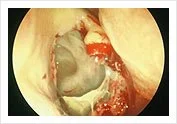
Intra-operative endoscopic drainage of the ethmoidal mucocele.
Cavity left alone to heal with good drainage and ventilation.
CT Scan after operation
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
Thorough evaluation of CT Scans are essential
Post-operative FESS cavity on CT Scan
These are post-operative endoscopic views of the ethmoidal cavity and post operative CT Scan of a clear completely healed ethmoid cavity.
Endoscopic View of Ethmoidal Cavity after FESS operation
Endoscopic Transnasal Central Skull Base Lesions
Pituitary tumour eroding the sphenoid sinus
Advanced Endoscopic Sinus Surgery can be performed for anterior and central skull lesions. The most common of which are pituary tumours.
MRI showing pituitary tumour eroding into the sphenoid sinus.
Tumors of the pituitary gland are routinely approached transnasally with an endoscopic technique as shown below.
Intra-operative Transphenoidal view of tumor
Post-operative view in the clinic 1 week after surgery
A panoramic view of the surgical field is obtained.
Post-operative tumor surveillance is possible in the clinic.
New Instrumentation in Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
Tru Cutting Instruments
Through Cutting Forceps
Advanced Endoscopic Sinus Surgery can be performed for anterior and central skull lesions. The most common of which are pituary tumours.
MRI showing pituitary tumour eroding into the sphenoid sinus.
Tumors of the pituitary gland are routinely approached transnasally with an endoscopic technique as shown below.
Mechanical Shaver
Tru-Cut forceps evolved with the use of a mechanical micro-debrider which cuts and sucks the diseased mucosa at the same time.
The removal of mucosa and bone is less traumatic, precise with less bleeding and minimal collateral tissue damage.
Tri-Cut Blades
Front Recess Instrument - Micro Debride
Surgical operating time is also lessened.
This technique is good for nasal polyps and edematous mucosa.
Micro-debriders are routinely used in FESS surgery today.
Surgical Navigation (Image Guidance System)
Endoscopic Navigation System for complex revision operations near the skull base. A navigation system with real time identification of location of instruments near the skull base.
A real-time surgical navigation device is available attached to an EM tracking blade for image guidance. This is surgical real time GPS.
May be necessary in complex revision endoscopic sinus surgery especially with skull base lesions.
Fusion ENT Navigation System with EM Tracking Blade