Suite 03-06 Gleneagles Medical Centre
6 Napier Road Singapore 258499
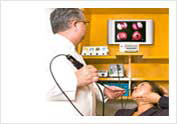 Flexible Endoscopic examination done in the Clinic
Flexible Endoscopic examination done in the Clinic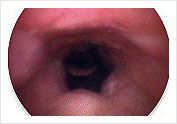 Collapsing Velopharyngeal Airway
Collapsing Velopharyngeal Airway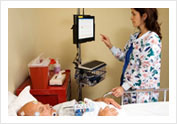 Overnight Sleep Study or Polysomnography at the Gleneagles Sleep Laboratory
Overnight Sleep Study or Polysomnography at the Gleneagles Sleep Laboratory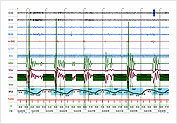 Obstructive Sleep Apnea Episode on PSG
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Episode on PSG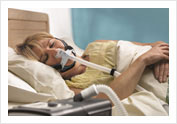 CPAP Therapy with Breeze Sleep Gear and Nasal Pillow
CPAP Therapy with Breeze Sleep Gear and Nasal Pillow Easylife Mask
Easylife Mask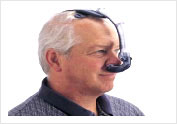
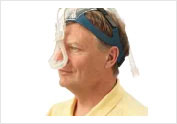 CPAP masks with Headgear
CPAP masks with Headgear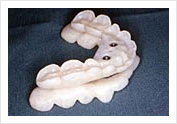
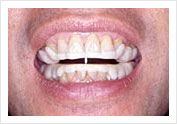 Dental Splint to widen the Oropharyngeal Airway.
To be worn when patient is asleep
Dental Splint to widen the Oropharyngeal Airway.
To be worn when patient is asleep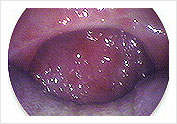
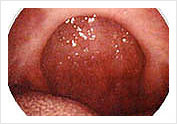 Results after Tonsillectomy and Uvulo-Palato-Pharyngoplasty for Snoring/Sleep Apnea view through mouth. The oropharygeal airway is widened and stiffened
Results after Tonsillectomy and Uvulo-Palato-Pharyngoplasty for Snoring/Sleep Apnea view through mouth. The oropharygeal airway is widened and stiffenedThe most difficult part of surgical therapy is that of choice of site of obstruction and method of surgery. To date most patients are evaluated by eye-balling the upper air way on endoscopy to determine the site or sites of obstruction. There are research tools to determine the site of obstruction, but these have not been proven to be reliable and reproducible to be a gold standard in the evaluation of OSA.