Suite 03-06 Gleneagles Medical Centre
6 Napier Road Singapore 258499
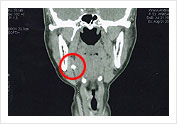 Submandibular Stone
Submandibular Stone 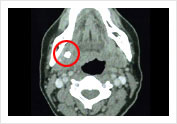 Submandibular Stone
Submandibular Stone 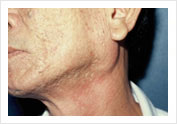 Parotid Tumor
Parotid Tumor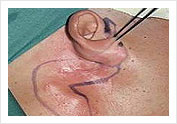 Recurrent Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid Gland with skin involvement
Recurrent Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid Gland with skin involvement 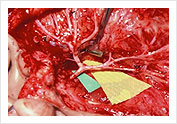 Facial Nerve Preservation after Total Parotidectomy
Facial Nerve Preservation after Total Parotidectomy